DevOps is a culture that maintains collaboration between Development and Operation. So it’s a combination of two words “Development” and “Operation”. DevOps aims to increase the organization’s speed to deliver an application from the development phase to production.
The development of an application is not as simple as people think. As everybody knows after development, the application needs to go under some phases like build, test, deploy, operate and monitor. Each phase has its standards.
In this post, we are going to set up a workflow using a few DevOps tools to manage and automate DevOps Lifecycle.
Prerequisites:
- Github
- Docker
- Docker Hub
- Docker-Compose
- Amazon AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Travis-CI
Workflow:
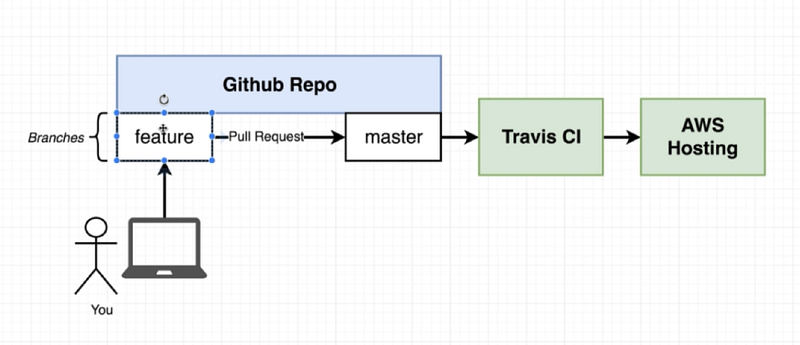
Step 1: Setup Github
Github is a version control system, that has many features when compared to other alternatives. Feel free to open an account on Github and share your project over it.
Step 2: Setup Travis-CI
Travis CI supports the development process by automatically building and testing code changes, providing user web dashboard to the success of the change.You can sign in with your Github account from the Travis-CI login page. After sign in you should enabling your project to build automatically under settings.
Travis CI: Test and Deploy with Confidence
Step 3: Setup Git
Git is an opensource version control system that provided under GPLv2, LGPLv2.1 license. You should check this link to install Git on your machine. There is clear documentation about how to install Git on the local machine.
Step 4: Setup Docker
 Docker is a precompiled software to automate and make it easier to build, test, deploy, operate and monitor by using container technology. To install and configure docker check docker documentation page. Docker-Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker base application. I strongly advice to read story that has written by Derian Pratama Tungka
Docker is a precompiled software to automate and make it easier to build, test, deploy, operate and monitor by using container technology. To install and configure docker check docker documentation page. Docker-Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker base application. I strongly advice to read story that has written by Derian Pratama Tungka
https://link.medium.com/otTe51c0WY
Step 5: Amazon AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Elastic Beanstalk is an AWS service that supports the development of web application. Elastic Beanstalk provides platforms for programming languages (Go, Java, Node.js, PHP, Python, Ruby), application servers (Tomcat, Passenger, Puma), and Docker containers. You can deploy your pre-compiled application using the management console, the CLI, or the API. Sommer Shurbaji has written two good stories about how to deploy docker base application to Elastic Beanstalk from Travis-CI and CLI. I added links.


