Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform has been released RHEL 8 Operating System.
Any workload. Any environment. One O.S. #RHEL8 is here. Learn more: https://t.co/6ZNWL5BQTc #RHSummit #RHEL pic.twitter.com/EjuqkUkR7s
— Red Hat, Inc. (@RedHat) 7 May 2019
Basically, this version of RHEL aims to improve the company’s position in the world of hybrid and multi-cloud environments, focus on automation and security, integration of high-quality deployment tools.
- Easy Configuration
- One command application installation
- Container development tools
- Open source projects (OpenShift, web tools, databases, etc.)
- Secure applications and systems
For this post, I’ll quickly recap RHEL 8 new features, installation process, RHEL 8 architecture, container tools, application stream, and other focused features.
1. Installation Process
There is nothing changed on the installation steps. Same graphical interface with the same steps as old versions.
A system that meets the following requirements:
- A 64-bit x86 or ARM machine
- 4 GB of RAM
- At least 20 GB of available disk space
2. Architecture and Repository
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 supports following architecture with supported kernel 4.18;
· AMD and Intel 64-bit architectures
· The 64-bit ARM architecture
· IBM Power Systems, Little Endian, IBM Z
RHEL 8 has three repositories;
- BaseOS
- Application Stream
- CodeReady Builder
2.1 Application Stream
The application stream is the next generation of Software Collection provides applications, databases, etc. AppStream has two types of package RPM and Module.
2.2 CodeReady Builder
Red Hat introduces a new repository the CodeReady Linux Builder. Developers may need while developing the RHEL base application.
3. Software Management
RHEL 8 offers a new tool named DFN(Dandified Yum) for package management instead of yum. DFN has better performance with support modular content. The new RPM version now validates the package content before starting the installation. DFN allows the user to install and upgrade package.
4. File Systems and Storage
The XFS file system now supports shared copy-on-write data extend functionality that allows sharing a common set of data blocks. It means everyone has a single shared copy of the file that links the same data blocks. This functionality allows minimizing the number of data blocks.
5. Tools
5.1 Cockpit
The cockpit is an opensource project that provides a user-friendly interface allowing for the remote administration of Red Hat enterprise linux server.
6. Container Tools
Linux containers are the key component of DevOps and microservices. RHEL 8 now includes container tools like; Buildah(container-building), Podman(running-container), Skopeo(sharing/finding containers) help developers to run and manage containerized applications more quickly and efficiently.
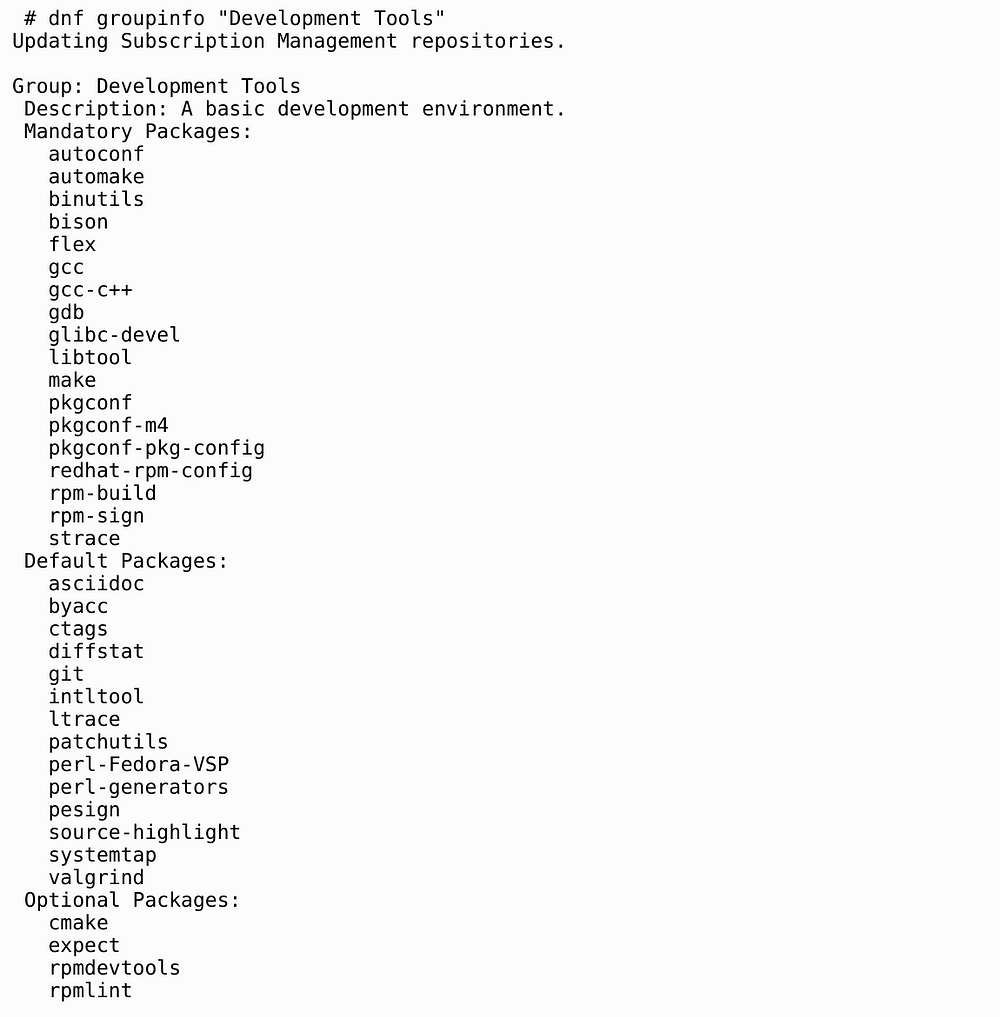
7. Development Tools
The following list shows available RHEL 8 development tools.
8. Application Versions
RHEL 8 includes multiple versions of databases, programming languages, compilers, web servers and other tools available for your use.

Linux/Unix Support | Linux And Unix Support Portal
Linux And Unix Support Portalcasesup.com

